Objectives
The objective of Sitepass release management is to:
- Define and agree on release and deployment management plans with stakeholders
- Ensure that the integrity of a release unit and its constituent components is maintained throughout the transition activities.
- Coordinate and maintain integrity of deployment to the live environment.
- Verify that all release units can be tracked, installed, tested, verified and /or uninstalled or rolled out.
- Ensure that organisation and stakeholder changes are managed during release and deployment activities.
- Record and manage the risks and issues related to new or changed service/requests and take necessary corrective action, and
- Review the preparation of release to ensure maximum successful deployments.
Service transition
What’s the role of service transition?
Service transition packages, builds, tests, evaluates, deploys, transfers or retires new or changed services or service components. It covers transition of new and changed services into supported environments such as release, planning, building, testing, evaluation and deployment. The purpose is to ensure that new, modified or retired services meet the expectations of the business from previous stages (service strategy and design).
Service transition includes the following processes:
- Transition planning & support
- Service asset & configuration management
- Change Management
- Release and deployment
- Service validation & testing
- Service evaluation, and
- Knowledge management
Release management’s objective is to align release plans with business projects and ensure that the release units are successfully built, tested, verified and deployed with minimal disruption to the live environment. It is a framework and is absorbed by organisations according to their processes and policies.
From Sitepass perspective, release management focuses on the development and release of new systems, features, functions and infrastructure that aligns to the product vision in order to meet our client needs and requirements.
Roles and responsibilities
The goal of release management as part of service transition is to deploy releases into the production environment and establish effective use of service in order to deliver value to the customer and be able to handover to service operations in this case our ‘clients’.
This process is responsible for delivering new functionality, whilst protecting the integrity of existing services through communicating the relevant information and changes and coordinating properly with the engaged teams and stakeholders. It is required to be implemented by attaining necessary approvals and supporting documentation.
Release management is a link between software development and its final deployment. It’s an intermediary step to ensure the reliability of the code and to certify that the deployed code meets the business and stakeholder’s expectations.
It’s a process which aids in delivery of new and improved product features built by the development team for our customers thereby providing efficient, scalable and reliable services which is tracked and appropriately documented with minimizing the risk of impact on availability of services.
There are various roles & responsibilities involved in release management, and for Sitepass these roles are:
| Roles | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Product Manager |
|
| Business Owners/Stakeholders |
|
| Development Leads/Business Analysts |
|
| Software Developers |
|
| Quality Analyst |
|
| Release Coordinator |
|
| Infrastructure and deployment team |
|
| Our employees |
|
| Clients and end user |
|
Release deployment strategy
Release strategy adopted at Sitepass leverages the below listed servers for developing product features, fixing bug fixes and deploying releases.
Infrastructure
The following table outlines the infrastructure used throughout the deployment strategy.
| Server | Branch | Description | Supported Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Development | n/a | Used by software developers for code creation and test/experiments etc | Locally available in Adelaide head office |
| Feature servers | Feature Branch | Used by development team to deploy code developed in feature branches, and utilised by QA team for feature testing | Single instance of each feature server serving the traffic, the code is being utilised to fulfil client requests/issues |
| Delta | Develop Branch | Used by development team for code creation, build etc. Additionally, used by QA team for sanity testing of features once those are fully tested in the feature server | Single instance of this server serving user traffic, the code is being utilised to fulfil client requests/issues |
| Alpha | Master Branch | Once the code is developed in delta its being moved to alpha to complete
the feature development for next release candidate to be merged in the master branch
Utilised for Hot fixes |
Single instance of this platform is currently available supporting client requests/issues |
| Beta | n/a | Is available and leveraged by the clients for testing of the platform. Also being leveraged internally by various business units for internal testing or demos. |
The server is hosted in Sydney AWS. |
| UAT | Release | This is utilised primarily by clients as part of user acceptance testing and is also used by internal QA team. | The server is hosted in Sydney AWS. |
| Production | n/a | Live environment where the code is released after successful deployment in
the Beta environment.
The code is primarily migrated from staging server, a standalone instance on AWS to both the production environment. |
The infrastructure architecture hosted out of Sydney AWS. |
Deployment sequence
The below diagram illustrates the code development stages used by the development team for code creation, build, merge and deployment.
- The code is first created on the local development servers, every developer has their own local instance on which they develop, test and experiment with the feature or bug fix.
- After the code is developed, it is deployed to the feature server for testing by the QA team. There are four feature server instance utilised by respective teams 1, 2, 3 and 4.
- A completed feature or bug is deployed to the delta server where the develop branch resides. On this environment the QA team will review, test and verify the bug fix in addition to performing sanity testing once the tested feature is moved from feature servers.
- Tested and completed code is then moved to Alpha which is home to the master branch. In the case of a ‘Hot Fix’ release and is further deployed to Beta and Production environment.
- In case of a minor/major release, the code is moved to UAT where the release branch from delta followed by deployment to Beta and Production environment.
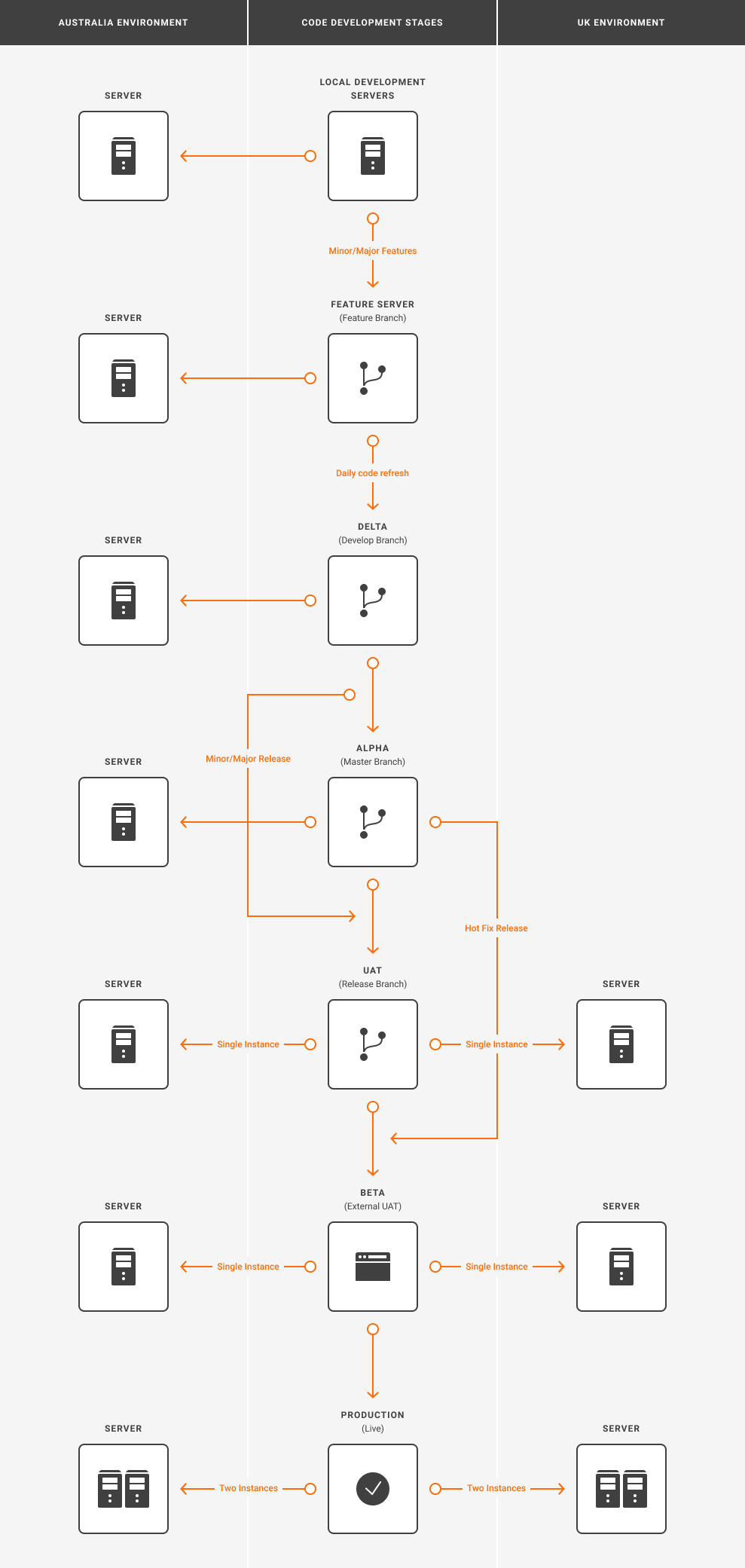
The above diagram illustrates the code development stages used by the development team for code creation, build, merge and deployment.
When release management occurs
Release management is a critical process for the deployment of new features, systems or infrastructure changes to Sitepass. The product development and management process employ a three-stage process of Planning, Development and Release. Whilst release management generally occurs towards the end of the process, it is involved in all stages within the process.
Planning
The planning phase of the product development process is to define the requirements for any new feature or infrastructure change that will be introduced. Feature suggestions, or new products that need to be developed to address business or client requirements are defined, scoped, analysed and during this period. Collaboration with clients and cross functional teams ensure a collective agreement towards the functions and impact of any new feature introduced.
Release Management within this phase, is leveraged to identify and manage the impact of this change through the identification of the following:
- The schedule for the release
- The existing use of the platform by end users
- Internal processes and documentation
- End user documentation and support materials
- Changes to sales contracts, schedules and pricing
- Version control
- Communication times and impact on service levels
- Size of quality assurance and time frames, and
- Changes to rollout and implementation plans.
Development
The development phase of the product development process is to build the features, systems or configure the infrastructure changes designed and agreed to through the planning phase. Most of the investment in time and resources is focused during the development phase, to build, test and finalise any features in preparation to be released.
Release management within this phase, is leveraged to manage the schedule and stage of each project in line with:
- Planned and agreed release schedules
- Level of quality assurance
- Completion of stories for project completion
- Addressing all critical bugs
- Infrastructure configuration state, and
- Code cut off
Release deployment
The release deployment phase of the product development process is where most release management activities occurs. As the final stage in the process, release deployment includes the activities which are central to the deployment of the product changes that are ready to be deployed to the production environment. Further information about this phase and the activities involved can be read in the release stages section.
Release monitoring and reporting
Releases are monitored and tracked by the release manager, and each release contains the following information:
- Release schedule – The dates the release moves through each stage of the process until it is deployed to the Beta and Production environments.
- Pre-deployment checklist – This comprises of activities initiated prior to deployment to production, such as code cut off schedule, documentation, release version updates etc.
- In deployment checklist – Tracking the actual deployment activities such as turning off/on monitoring tools, status page verification, executing the release script etc.
- Post deployment checklist – Consisting of updating the status of the release and following the release communication plan.
- Signoff approvals – Comprises of tracking sign off from key stakeholders.
- Feedback and actions – Records the lessons learned and feedback for the release to ensure continuous improvement.
Release measurement & metrics
Key performance indicators (KPI)
Below are some of the key performance indicators for release management:
| KPI | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of major releases | This KPI is established based on release type and is evaluated as a high-risk release depending on the coordination involved between various functions and teams. These releases will usually be scheduled based on long-term vision and backlog items. |
| Number of minor releases | This one is also factored on the release type and will be measured against scope of small but critical changes implemented. These will usually occur on quarterly basis. |
| Number of hot fix releases | Hot fix is typically a low priority release comprising of bug fixes and is often released weekly. |
| Number of emergency release | With the prevailing service levels, emergency releases are unexpected with the scope extending from an urgent client request to a critical security patch implementation. |
| Number of outages/incidents caused by a release | Any outage caused during a release should be tracked and documented for better planning of releases |
| Number of tickets/issues successfully resolved in a release | Is calculated against the number of tickets/issues addressed/fixed during a release. |
| Number of tickets/issues that didn’t resolve in a release | This will account for number of tickets/issues that did not get fixed in a release leading to creation of additional tickets. |
| Total release downtime | The difference between the estimated downtime and the actual downtime during a release. |
| Unit Test Cases | Number of unit test cases covered for code creation |
Critical success factors (CSF)
Below are some of the critical success factors for release management:
- The release should be quality driven with better software/product/hardware
- Improved frequency of releases aligned with business needs
- Seamless implementation
- Releases should be measured i.e. successful/failed releases
- The released product/feature should be usable
- The released product/feature should be in conformance with the business request
- Release delivery timelines should be kept in check
- All the necessary communication and training should be in place
Benefits of release management
Below are some of the benefits of the introduction of release management for Sitepass:
- Faster response time – With shorter frequency of releases and delivering services to customers, various development and deployment processes are streamlined thereby realising the benefits of changes as quickly as possible
- Enhanced flexibility and agility – With availability of consistent information, the impact of emerging changes can be easily accommodated to the release schedule.
- Increased productivity – Through the creation and classification of release types and formation of various processes, there will be quicker developments.
- Increased collaboration – With involvement of various teams in the activities of release management with constant communication and information sharing, all the teams will have timely and clear insights into the schedule, changes and status of the releases.
- Risk mitigation – With high visibility in the product governance releases can be planned seamlessly and enable the stakeholders to mitigate any potential risk of release failure.
Release classification and versioning
We continuously introduce improvements to our products, services and platform in order to meet the business requirements and maintain infrastructure stability and security.
Refer to service levels for a list of release classifications, notification periods and versioning.
Release stages
Below stages occur throughout the release management process, the stages may vary for each release classification, however the workflow stages will remain as follows:
- Release planning
- Release impact assessment
- Regression testing & finalising development
- Release readiness review
- Release communication & documentation
- Release signoff
- Release deployment, and
- Post Release verification & review
Release planning
Release planning is a collaborative effort involving the product owner, business analysts, release coordinator and development teams to plan the deliverables for a particular release.
Release impact assessment
This stage focuses primarily on assessing the impact of issues/features going in to a release:
- To assess any impact on our existing customers to make sure they are kept well informed
- To see any new features impact on the product pricing
- If any change is required in the pricing schedules
- To ensure if any marketing efforts are required to introduce a feature/enhancement
- Any internal process and knowledgebase documentation changes are required.
- What new features need to be included in webinars or internal product training.
- Release should be in line with the defined platform service levels
- The impact of the change to existing customers, and how they are using the system
- Batching updates for the implementation team, and
- Any changes to integration code that may impact integration solutions.
Regression testing and finalising development
This stage comprises focuses on finalising the product developments by:
- Fixing all in development issues,
- Following up on PO/Reporter tickets,
- Identify any blockers/major issues (if any),
- Ensure that as quality assurance regression testing is performed,
- Conduct necessary UAT, and
- Resolving any identified regression issues.
Release readiness review
In this stage, the release coordinator coordinates with the following teams to ensure that the relevant activity is fulfilled to prepare for the release.
| Team | Activity |
|---|---|
| Sales | To ensure all the product pricing changes are complete (if any) |
| Review schedules | Any changes in schedules are complete |
| Production | Any new improvements involving support requests creation should be well communicated and understood by the team |
| Marketing | To see if any improvements/changes require marketing efforts |
| Client Services | To ensure that the team is aware of the new changes being rolled out |
| Client | To communicate all the changes to the client and verify if any external training is required |
| User Acceptance Testing | Ensure a sign off is obtained on UAT from the client services team |
Release communication & documentation
This stage seeks the necessary updates to the documentation informing end users and internal employees about the release changes. Below are the listed components:
| Component | Reference site |
|---|---|
| Knowledgebase | https://support.mysitepass.com |
| Release notes | https://release.mysitepass.com |
| Status Page Notifications | https://status.mysitepass.com |
Release signoff
In this stage sign off is attained from all the key stakeholders to ensure the release is ready to be deployed.
Release deployment
This stage comprises of the below activities initiated to perform the actual deployment along with administering the release through:
- Code cut off
- Executing the release script and deploying the updates to each environment
- Verify status page status
- Updating the release schedule
- Updating the release version status
- Updating the release status
Post release verification and review
Post release review records the lessons learned and/or any feedback for the release or any of its stages/steps. It involves hosting joint reviews for the teams to share feedback.


